Last Updated on April 8, 2023 by Francis
Dreams are mysterious phenomena that have long been of interest to psychologists. They have been studied for centuries, yet their meaning and purpose remains largely unknown. From scientific studies to Freudian interpretations, the psychology of dreams has been a source of fascination for many. In this article, we will explore what dreams are in the field of psychology and how they are studied.
Contents
What is the Role of Dreams in Psychology?
Dreams have been a source of fascination for people since the ancient times. In psychology, dreams are studied to understand the inner workings of the mind and the way in which it processes and stores information, as well as to determine the role that dreams play in mental health and well-being. Dreams can be seen as a window into the unconscious and can provide insight into one’s thoughts, feelings, and motivations. They can also serve as a form of problem-solving by allowing the dreamer to explore creative solutions to difficult situations.
The study of dreams has been an important part of psychology since the early days of the discipline. Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, believed that dreams could provide insights into the unconscious mind. He proposed that dreams are a means of expressing repressed desires and fears, and that they are a way of symbolically representing unresolved conflicts. In modern psychology, dreams are studied using a variety of techniques, such as dream diaries, dream interpretation, and dream recall.
The Brain and Dreams
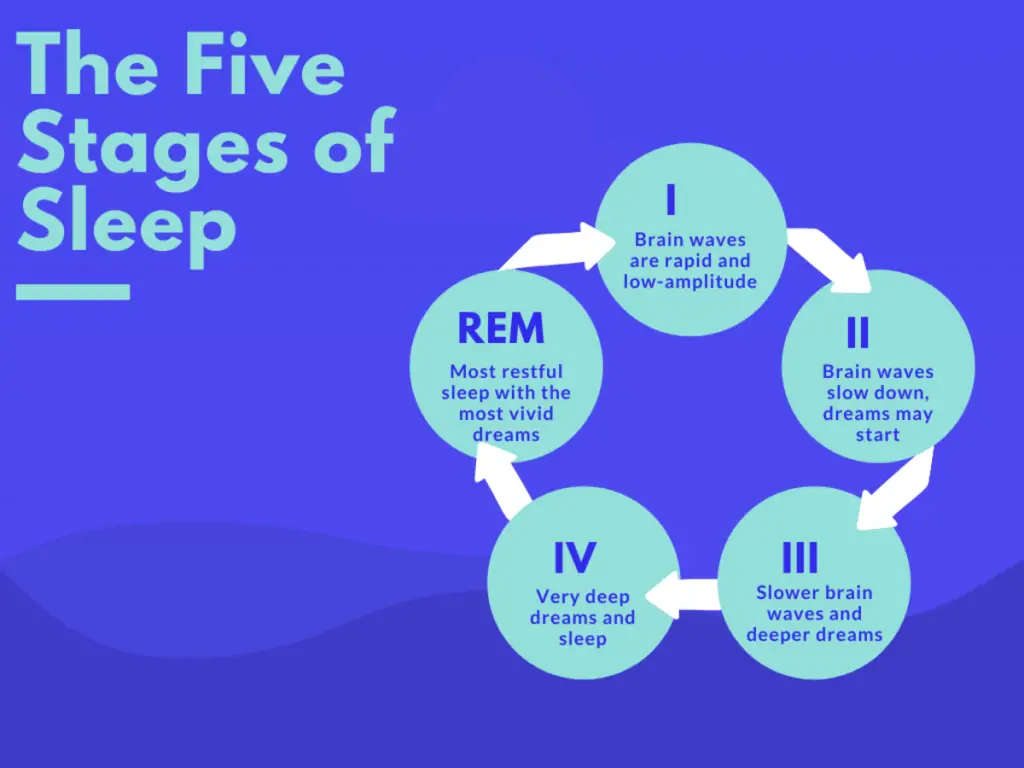
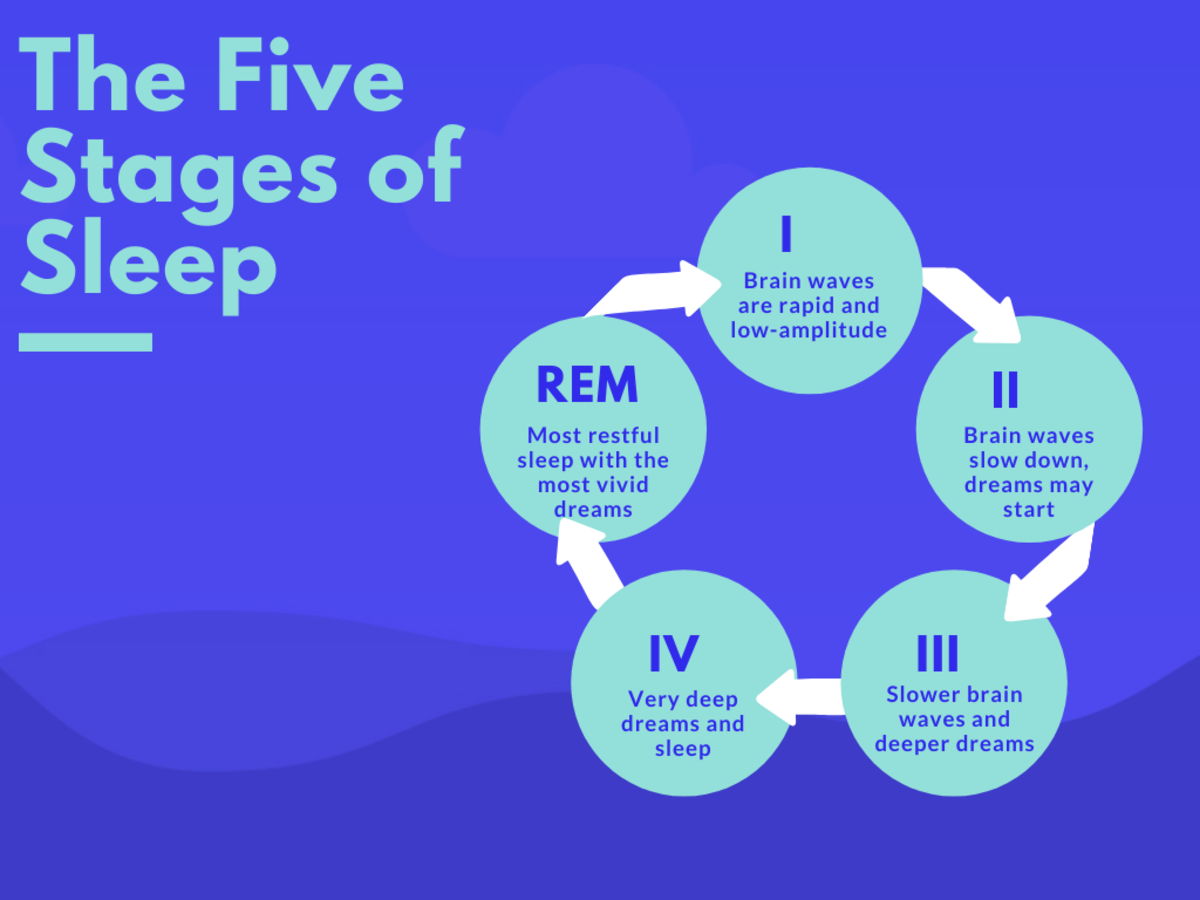
The brain is the organ responsible for generating dreams. During the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep stage, the brain is most active and produces vivid and intense dreams. During this stage, the brain is believed to be processing information and forming memories. Studies have shown that the brain is able to access information from the past and present and use it to create dream scenarios.
Neuroscientists have also studied the physiological mechanisms of dreaming. They have found that certain areas of the brain are more active during REM sleep, including the frontal lobe, the hippocampus, and the thalamus. This increased activity is believed to be responsible for the vivid imagery and emotion of dreams.
Psychological Theories of Dreams
Psychologists have developed a variety of theories to explain the purpose and meaning of dreams. Sigmund Freud proposed that dreams are a form of wish fulfillment and that they can provide insight into the unconscious mind. Other psychoanalytic theorists, such as Carl Jung, proposed that dreams are a form of self-expression and can provide insight into the collective unconscious.
Behaviorists believe that dreams are a form of problem-solving and that they can help the dreamer to find creative solutions to difficult situations. Cognitive psychologists believe that dreams are a result of the brain’s attempt to process and store information. Finally, evolutionary psychologists believe that dreams may have an adaptive function and may help the dreamer to process and respond to environmental cues.
Dream Interpretation
Dream interpretation is the process of assigning meaning to dreams. It is often used as a therapeutic tool to help the dreamer gain insight into unresolved issues and to explore creative solutions to problems. Dream interpretation is based on the idea that the dreamer is the best authority on the meaning of their dreams.
Dream interpretation is often done in the context of psychotherapy. In this setting, the therapist helps the dreamer to explore the meaning of their dream and to make connections between the dream and their current life. The therapist may also suggest ways in which the dreamer can use their dream to work through difficult issues or to gain insight into their behavior and motivations.
Dream Symbolism
Dreams often contain symbols that are representative of the dreamer’s thoughts and feelings. Symbols can take many forms, such as people, objects, animals, and settings. In dream interpretation, symbols are used to uncover the dreamer’s unconscious thoughts and feelings. For example, a dream about a snake may represent fear or hidden danger.
Dream Analysis
Dream analysis is the process of exploring the meaning of a dream. It is often done in the context of psychotherapy, where the therapist works with the dreamer to uncover the symbolism of the dream and its connection to the dreamer’s life. Dream analysis can be used to gain insight into unresolved issues and to explore creative solutions to problems.
Related Faq
What is Dream in Psychology?
Answer: Dream in psychology is the study of how dreams influence our behavior, thinking and emotions. Dreams are thought to be a form of communication from the unconscious mind, providing insight into our innermost thoughts and feelings. Dreams can be used therapeutically to help people process difficult emotions and gain insight into their lives. Researchers have found that the content of dreams can be related to a person’s mental state and can provide valuable insights into their mental health.
What is the Role of Dreams in Psychology?
Answer: Dreams play a role in helping us to process difficult emotions and gain insight into our lives. They are thought to be a form of communication from the unconscious mind, reflecting what is going on in our lives and allowing us to gain valuable insight into our deepest thoughts and feelings. Dreams can also provide useful information about our psychological state, helping us to understand our mental health and gain insight into our behavior.
What Are Common Themes in Dreams?
Answer: Common themes in dreams include falling, flying, being chased, feeling trapped or lost, being unprepared for a test, being naked in public, and being late. Other common dream themes include being attacked or pursued, finding a hidden object or secret, being in a frightening place or situation, and being confronted with a difficult decision. Dreams can also include elements of past memories, future fears, and fantasies.
What Are the Benefits of Studying Dreams?
Answer: Studying dreams can provide valuable insight into our mental state and can help us to gain a better understanding of our behavior. Dreams can also help us to process difficult emotions and gain insight into our lives. Studying dreams can also help us to become more aware of our unconscious thoughts and feelings, giving us insight into how our unconscious mind works.
What is the Difference Between a Lucid Dream and a Normal Dream?
Answer: A lucid dream is a dream in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and may be able to control their dream environment and actions. In contrast to a normal dream, the dreamer in a lucid dream is aware that the dream is not real and can consciously choose what actions to take. Lucid dreaming can be beneficial in helping to process difficult emotions and gain insight into the unconscious mind.
What Are Some Techniques for Enhancing Dream Recall?
Answer: There are several techniques for enhancing dream recall. Keeping a dream journal can help to increase dream recall by providing a place to record dreams and helping to trigger memory of past dreams. Keeping a regular sleep schedule and sleeping in a dark and quiet environment can also help to improve dream recall. Taking time to relax before sleeping and visualizing a desired dream can also help to enhance dream recall.
Dreams in psychology are an incredibly important part of understanding the human mind. They allow us to explore our innermost thoughts and feelings, and give us insight into our subconscious. By understanding the meaning of our dreams, we can gain insight into our own emotions, behavior, and motivations. Through understanding our dreams, we can better understand ourselves and the world around us. Dreams are a powerful and often overlooked tool for self-exploration and personal growth.