Last Updated on March 31, 2023 by Francis
As a society, we have long held up the notion that intelligence is a measure of one’s success. We may not always agree on what constitutes intelligence, but most of us can agree that having a higher IQ is generally perceived as an advantage. But what happens when one of the most important senses, hearing, is taken away? Does being deaf affect IQ? In this article, we will explore the potential impact of deafness on intelligence and how it might affect a person’s life.
No, being deaf does not affect the IQ of a person. Deafness is not a learning disability, and deaf people have the same range of intelligence as anyone else. Deaf people have the same ability to learn, solve problems, and think abstractly as hearing people. In fact, deaf people can achieve success in many areas, like academics, sports, and business.

Contents
Does Being Deaf Affect IQ?
Introduction
It is a common misconception that being deaf affects a person’s intelligence quotient, or IQ, but the truth is that there is no scientific evidence to support this belief. Instead, the impact of hearing loss on cognitive abilities is more likely to be due to the effects of social, educational, and cultural factors. This article will explore the impact of deafness on IQ and debunk the myth that deafness automatically leads to a lower IQ.
The Impact of Deafness on Cognitive Ability
While there is no scientific evidence to suggest that deafness directly affects IQ, there is evidence to suggest that it can have an indirect impact on cognitive abilities. Studies have shown that children who are born deaf or become deaf at a young age are at a disadvantage when it comes to language acquisition, which can lead to delays in thinking and problem-solving skills. Furthermore, those who are born deaf and do not receive proper education and support may not be exposed to the same cognitive stimulation and resources that hearing children are, which can result in a lower IQ.
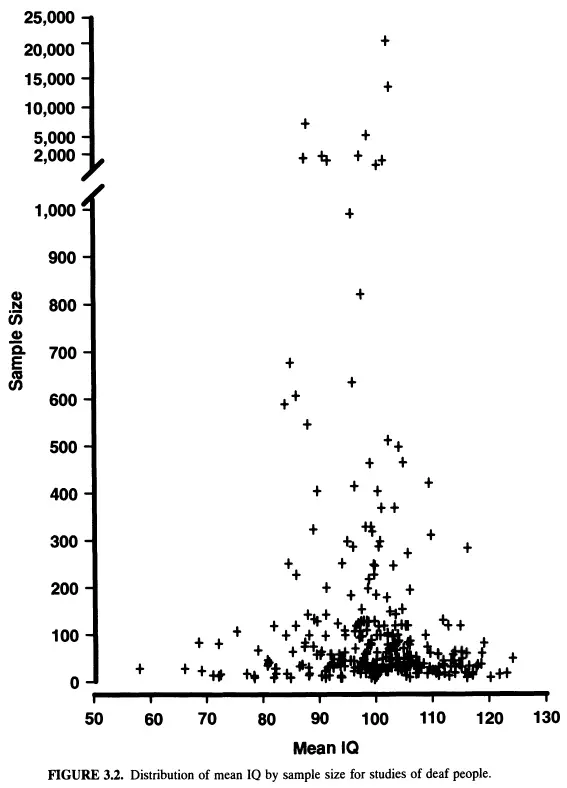
However, it is important to note that this does not mean that all deaf individuals have a lower IQ than their hearing peers. Studies have shown that, when given the same educational opportunities, deaf individuals can achieve the same cognitive levels as their hearing peers. Furthermore, deaf individuals have been found to have higher IQs than the general population, suggesting that hearing loss does not necessarily lead to a lower IQ.
The Role of Education in Cognitive Ability
It is important to note that the impact of deafness on IQ is more likely to be due to the effects of social, educational, and cultural factors than to the hearing loss itself. Studies have found that educational opportunities play a significant role in cognitive development, and those who are born deaf and do not receive proper educational support may not reach their full cognitive potential. For example, one study found that students who were taught in sign language reached higher levels of cognitive abilities than those who were taught orally.
Furthermore, those who are born deaf may not have the same access to language and communication resources that hearing children have, which can result in delays in language acquisition and cognitive development. In addition, those who are deaf may be at a disadvantage when it comes to social interaction, which can also have an impact on cognitive abilities.
The Impact of Cultural Factors
In addition to educational factors, cultural factors can also play a role in cognitive development. Deaf individuals who are born into hearing families may not have access to the same language and communication resources as those who are born into deaf families. This can result in language delays and a lack of exposure to certain cognitive stimulation and resources, leading to a lower IQ.
Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that those who are born deaf may be at a disadvantage when it comes to educational opportunities due to discrimination and stigma. Deaf individuals may be excluded from certain educational opportunities or may be discouraged from pursuing an education, which can lead to lower cognitive abilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there is no scientific evidence to suggest that deafness directly affects IQ, there is evidence to suggest that it can have an indirect impact on cognitive abilities. The impact of deafness on IQ is more likely to be due to the effects of social, educational, and cultural factors than to the hearing loss itself. Those who are born deaf may not have access to the same language and communication resources that hearing children have, which can result in delays in language acquisition and cognitive development. Furthermore, those who are born deaf may be at a disadvantage when it comes to educational opportunities due to discrimination and stigma.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Does being deaf affect IQ?
A1: Generally speaking, being deaf does not affect IQ. Studies have shown that deaf children have IQ scores similar to their hearing peers. However, there are a few studies that suggest that being deaf could potentially lead to a lower IQ. One study found that hearing-impaired individuals had a lower IQ than those with normal hearing, while another study reported that the IQ of deaf individuals was lower than the IQ of their hearing peers. Additionally, studies have indicated that a person’s IQ may be influenced by the quality of their early educational experiences, so it is possible that children who are deaf may not receive the same quality of educational experiences as their hearing peers, leading to a lower IQ.
Q2: Are there any cognitive effects of being deaf?
A2: There are a few cognitive effects of being deaf. For example, research has suggested that deaf individuals may have difficulty processing and understanding verbal information. Additionally, deaf individuals may have difficulty understanding certain types of nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language. Additionally, studies have suggested that deaf individuals may have difficulty with executive functioning skills, such as problem solving, working memory, and planning.
Q3: What are the educational implications of being deaf?
A3: Being deaf can have a variety of educational implications. For example, deaf individuals may need to learn communication strategies, such as sign language, in order to effectively communicate with others. Additionally, deaf individuals may need accommodations in order to participate in classroom activities, such as special seating arrangements, assistive technology, and visual aids. Furthermore, deaf individuals may need additional support in order to understand and process verbal information.
Q4: How do deaf individuals learn?
A4: Deaf individuals learn in a variety of ways. For example, many deaf individuals learn through visual methods, such as reading, watching videos, and using other visual aids. Additionally, many deaf individuals learn through tactile methods, such as haptic technology, tactile diagrams, and tactile boards. Additionally, many deaf individuals learn through signing, either with a teacher or with other deaf individuals.
Q5: Is there a difference between being hard of hearing and being deaf?
A5: Yes, there is a difference between being hard of hearing and being deaf. Generally speaking, individuals who are hard of hearing have some residual hearing, while individuals who are deaf have no residual hearing. Additionally, individuals who are hard of hearing may be able to use assistive technology, such as hearing aids and cochlear implants, to help them to hear, while individuals who are deaf generally cannot use such technology.
Q6: How does being deaf affect daily life?
A6: Being deaf can have a variety of effects on daily life. For example, deaf individuals may need to use sign language or other forms of communication in order to effectively communicate with others. Additionally, deaf individuals may need to use assistive technology, such as hearing aids and cochlear implants, in order to hear. Furthermore, deaf individuals may face challenges in accessing certain types of information, such as verbal instructions, which can make it difficult for them to participate in certain activities. Additionally, deaf individuals may face social and cultural barriers that can make it difficult for them to participate in activities or form relationships.
Deaf People Answer Commonly Googled Questions About Being Deaf
In conclusion, being deaf can have some impacts on an individual’s IQ, but these impacts depend on a range of factors, including the individual’s level of exposure to language, the quality of their education, and the resources they have available. It is clear that, while there may be some correlations between deafness and IQ, these correlations are not absolute and can be influenced by a variety of outside factors.